
Difference: FRCVBatteryBoosterPack (5 vs. 6)
Revision 62017-07-07 - MaggieGates
| Line: 1 to 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Battery Booster Pack for Mobile Robots P3-AT | |||||||||||
| Line: 7 to 7 | |||||||||||
| This project started as a way to support the need for more power longevity during testing and as a way to utilize batteries several sizes too large that were accidently ordered. The batteries used for this pack were three 12V 12AH Lead Acid Casil Batteries about 4” by 6”. While these batteries were several inches too large to fit in to the robot itself, the voltage and current were compatible enough that they could easily be added in parallel to the standard batteries used. | |||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE1 HERE) | ||||||||||
| > > | |||||||||||
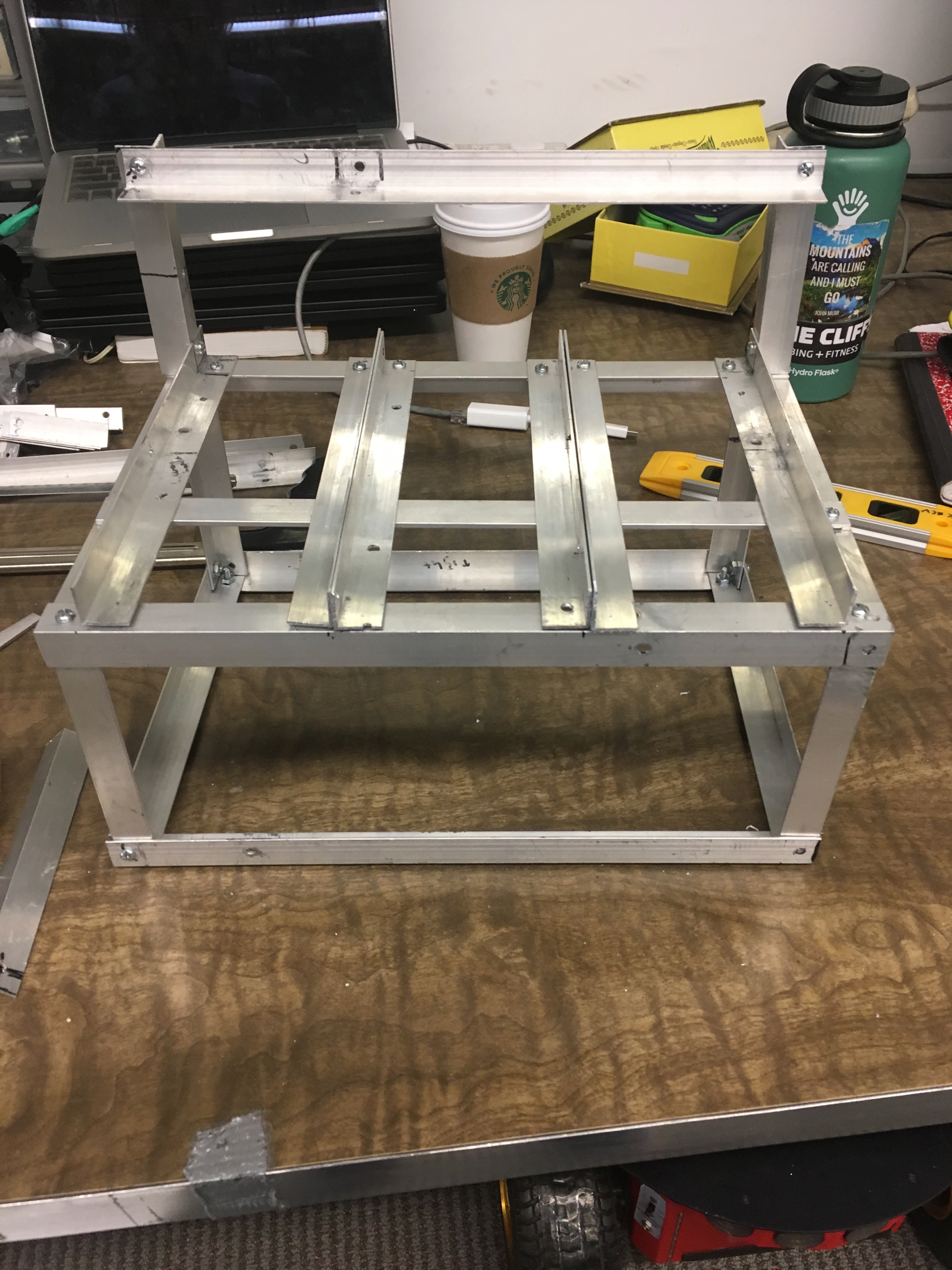
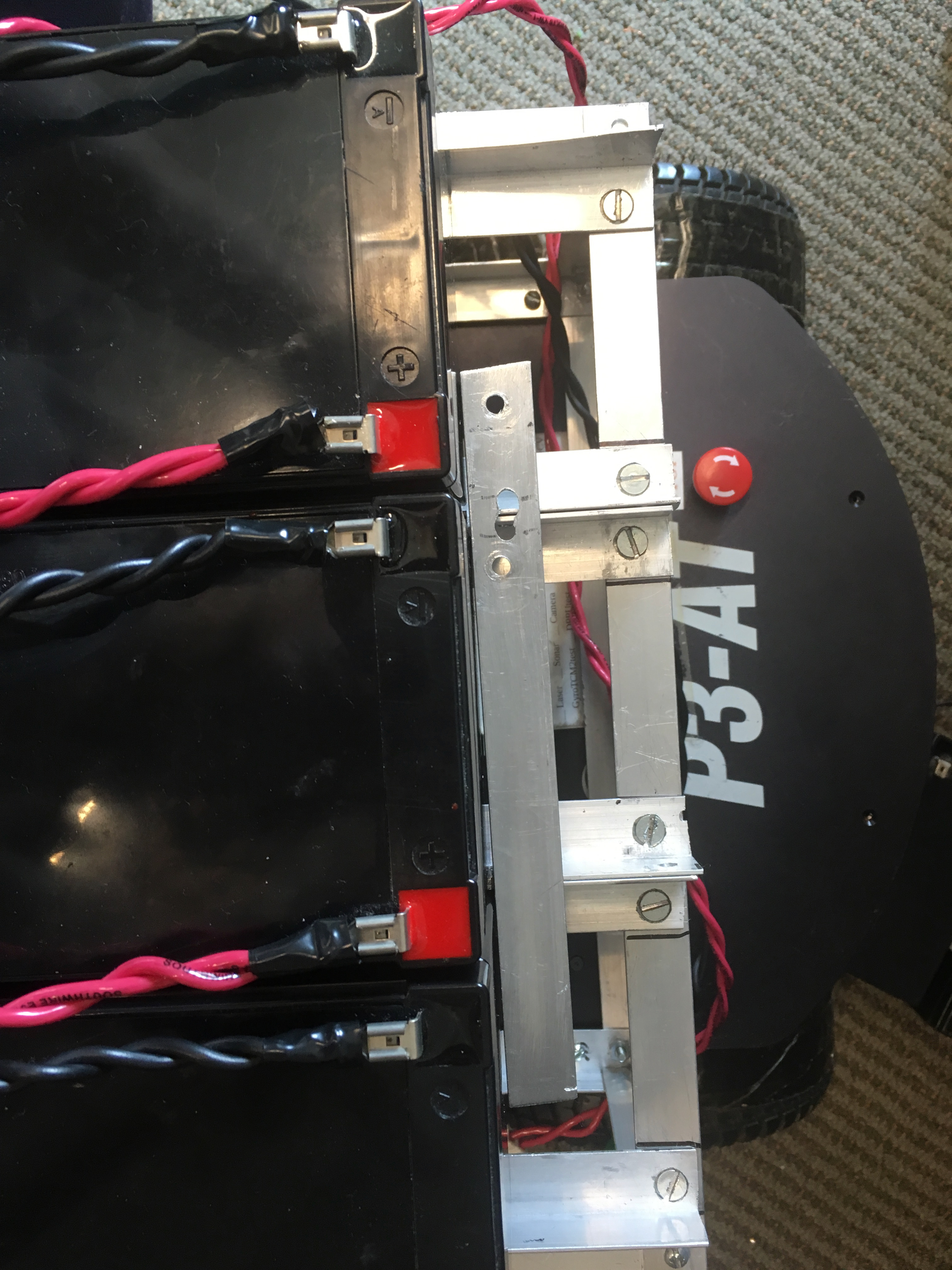
The Mount | |||||||||||
| Line: 16 to 16 | |||||||||||
| The dimensions of the base are: 13.5" wide x 9.25" long x 5.5" tall. The battery rails are 7.25” long and 4”apart with a flat bar attached underneath the rails for extra support. | |||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE2) | ||||||||||
| > > |  | ||||||||||
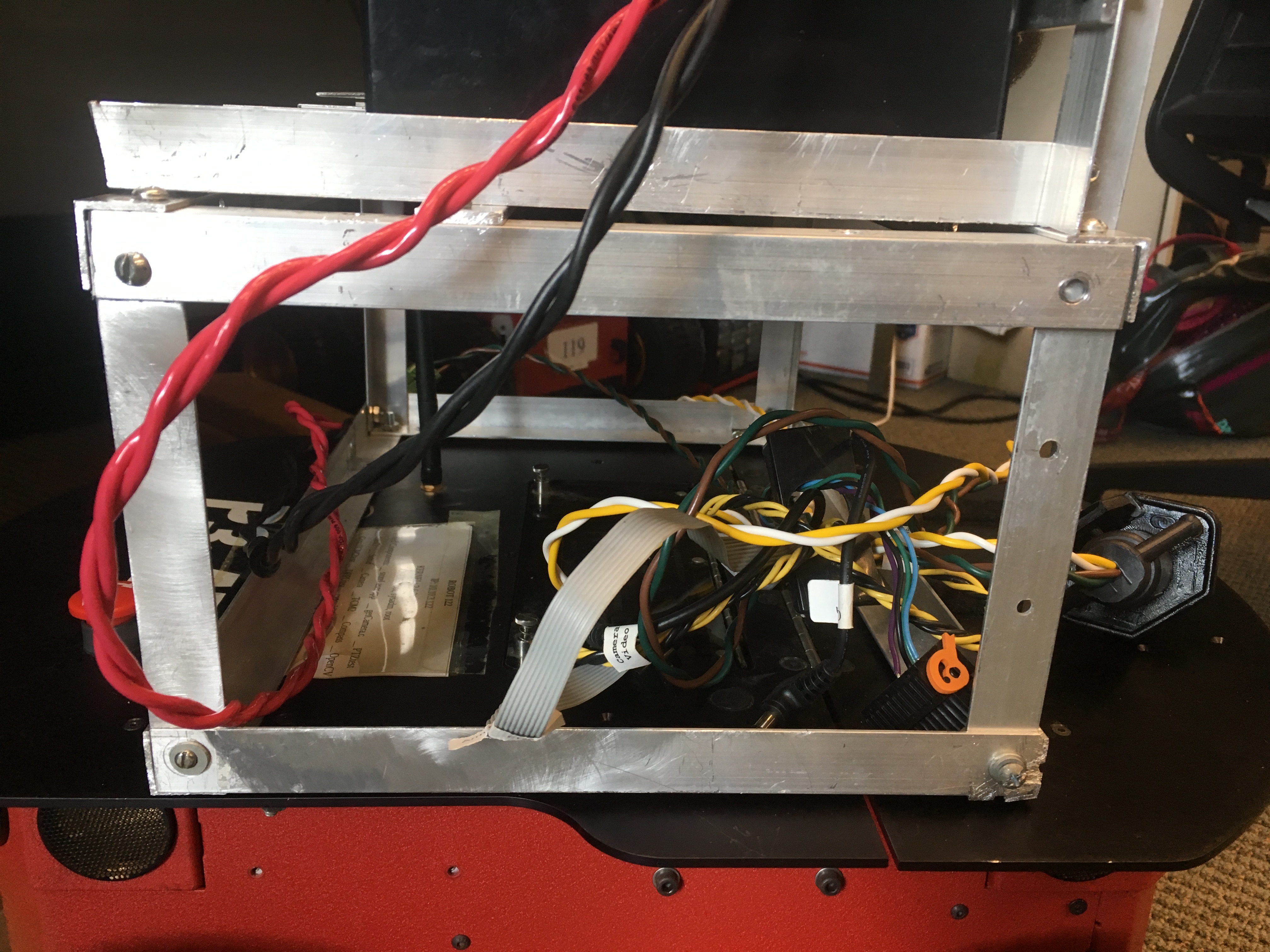
The Wiring | |||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE3)(PICTURE4) | ||||||||||
| > > | | ||||||||||
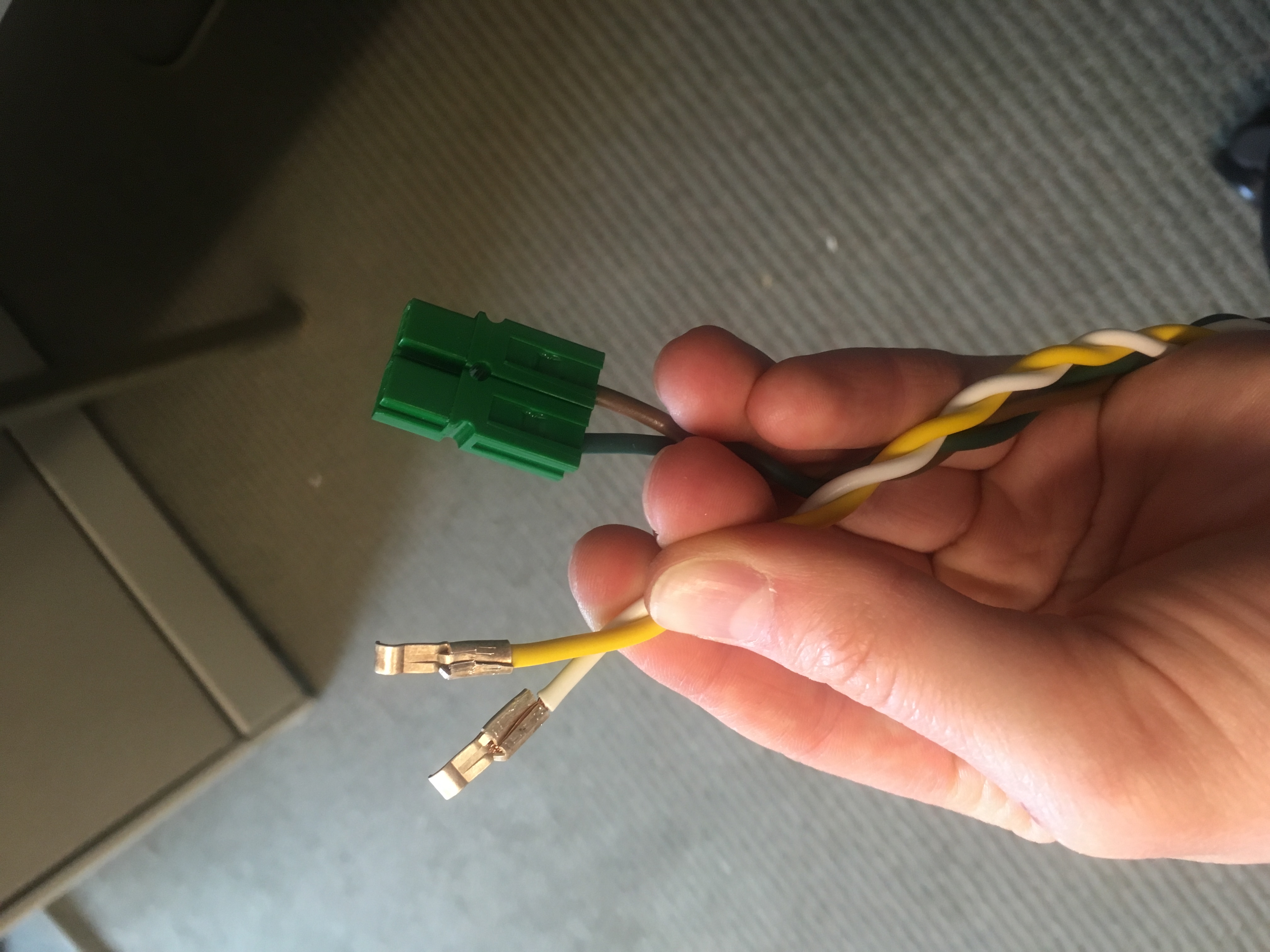
| For the wiring we used two strands of size 8 electrical wire twisted together and soldered to bared female spade connectors, wrapped in electrical tape. Each section of wire was connected by wire nuts. | |||||||||||
| Line: 30 to 30 | |||||||||||
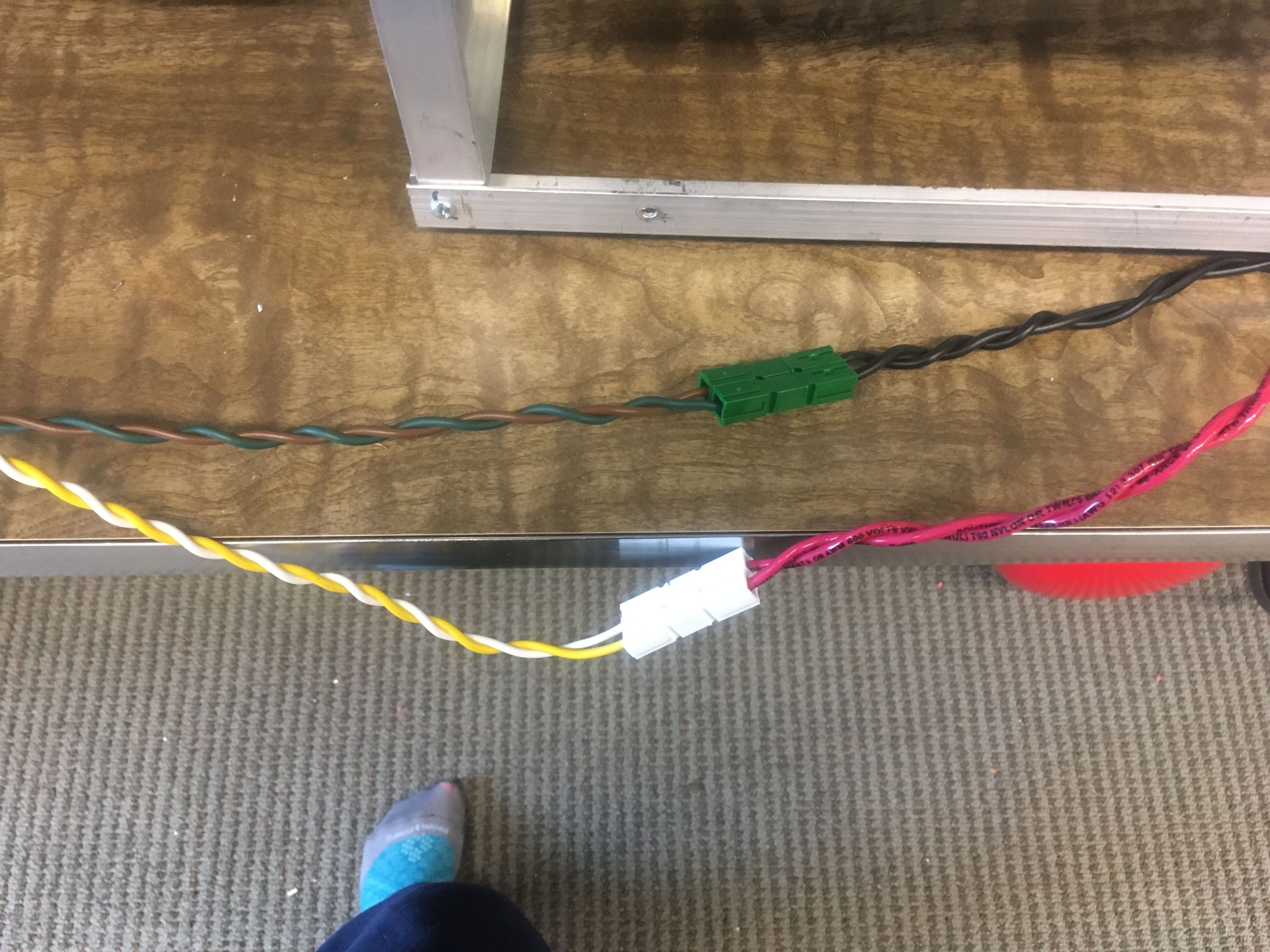
| We cut the wires of the RV connector in the middle and connected the wires on the male end to the loose ends of the batteries’ wires with powerpole stackable connectors. | |||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE5)(PICTURE6) | ||||||||||
| > > |   | ||||||||||
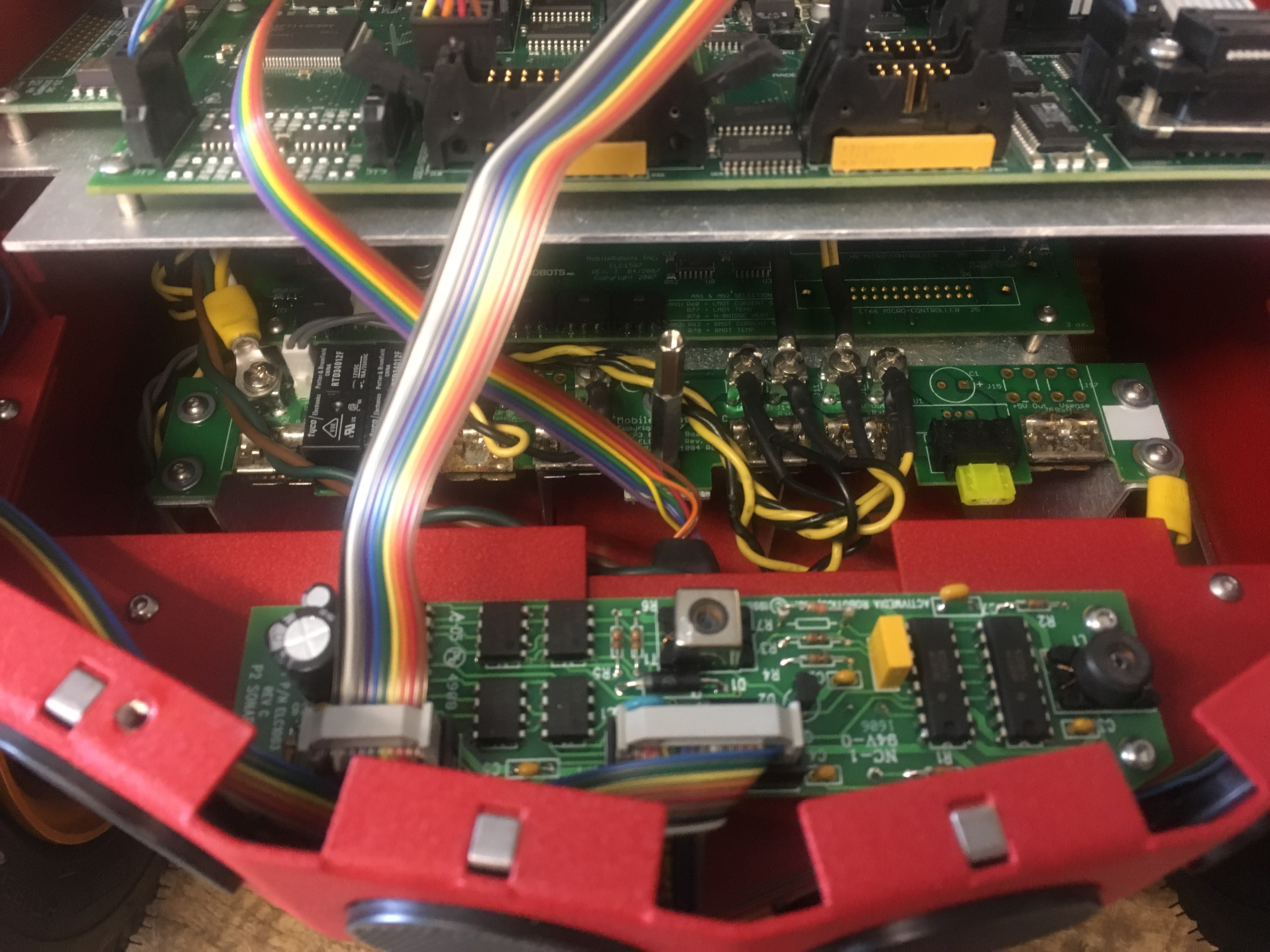
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | In order to connect the wires stemming from the female end to the bot itself we bared the wires and crimped those on to ring tongue connectors which we then screwed in to a positive (pictured left) and negative (pictured right) connection on the robot’s battery strip. | ||||||||||
| > > | In order to connect the wires stemming from the female end to the bot itself we bared the wires and crimped those on to ring tongue connectors which we then screwed in to a positive (pictured left) and negative (pictured right) connection on the robot’s battery strip. | ||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE7)(PICTURE8) | ||||||||||
| > > |    | ||||||||||
The Entire Setup | |||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | (PICTURE9) | ||||||||||
| > > | 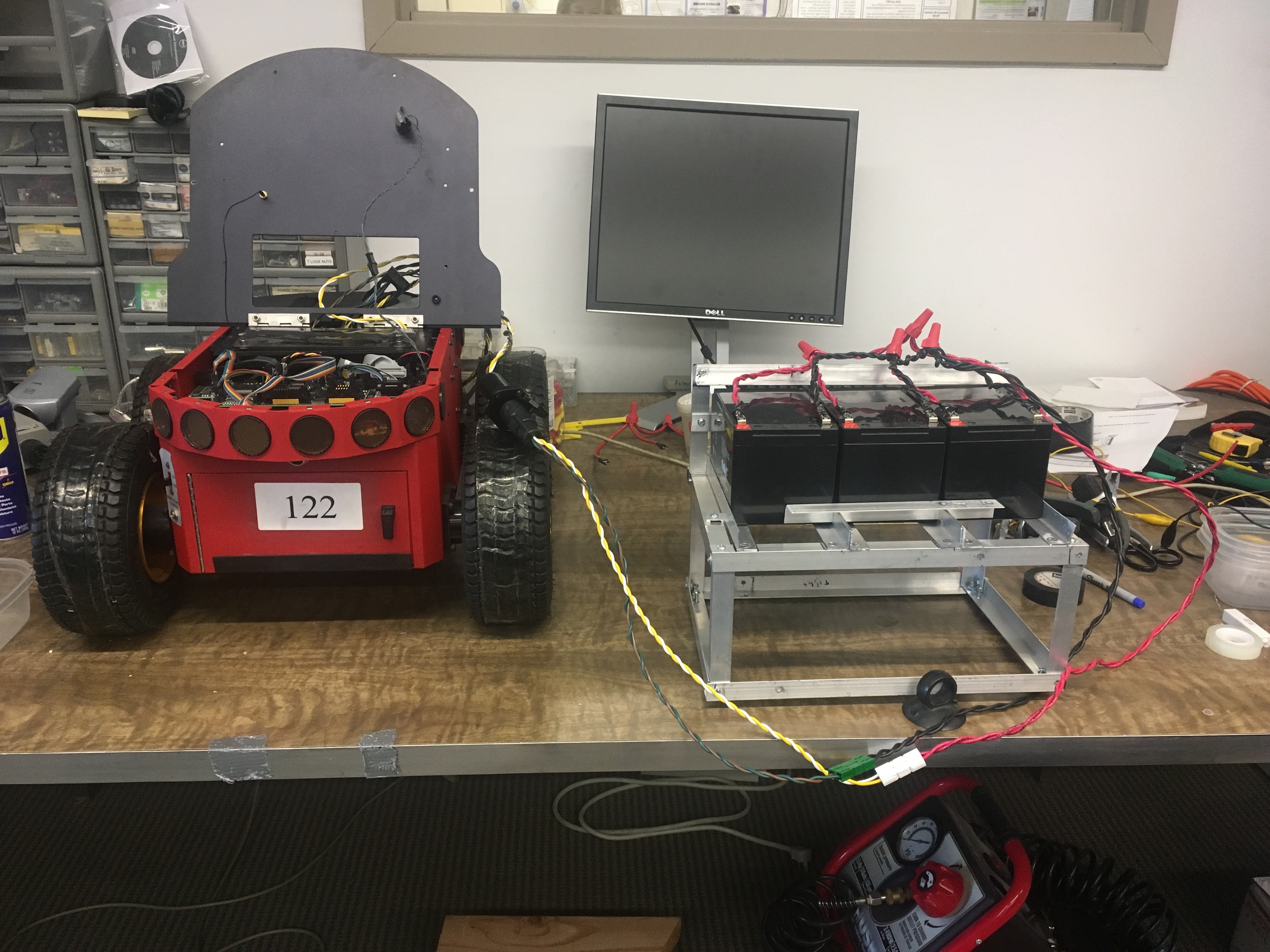    | ||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||
| < < | This booster pack more than doubled the life span of the robot during intensive testing. Video of testing can be found at https://twiki.ace.fordham.edu/bin/view/Main/FRCVBatteryBoosterPack | ||||||||||
| > > | TestingThis booster pack more than doubled the life span of the robot during two phases of testing. The first phase of testing consisted of infinitly looping through turns and direction changing. The robot was rasied on a box so that the teh wheels weer of the ground. Its left and right wheels moves in opposing directions for a set period of time and then changed directions until the battery was drained. Un-boosted the battery lasted about 4 hours, with the boosted the batteries lasted about 8 hours. There is some room for error as the the the length of the boosted bot's test run required it to be stopped, turned off, and restarted during lab occupancy intervals. The second phase of testing involved running a bot without the pack and bot with the booster pack in demo mode in an enclosed psace running object avoidance using the laser and sonar. The un boosted lasted roughly 2 hours while the boosted bot lasted roughly 4.5 hours. Video of testing can be found in the included attatchments below labeled: "Testing_of_Booster_Pack" | ||||||||||
Permissions | |||||||||||
| Line: 67 to 76 | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Added: | |||||||||||
| > > |
| ||||||||||
View topic | History: r7 < r6 < r5 < r4 | More topic actions...
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback